Introduction
Optical fiber is used as the temperature conducting medium with the distributed optical fiber temperature measurement system based on Raman scattering to measure the temperature field distribution in continuous space along the direction of optical fiber.

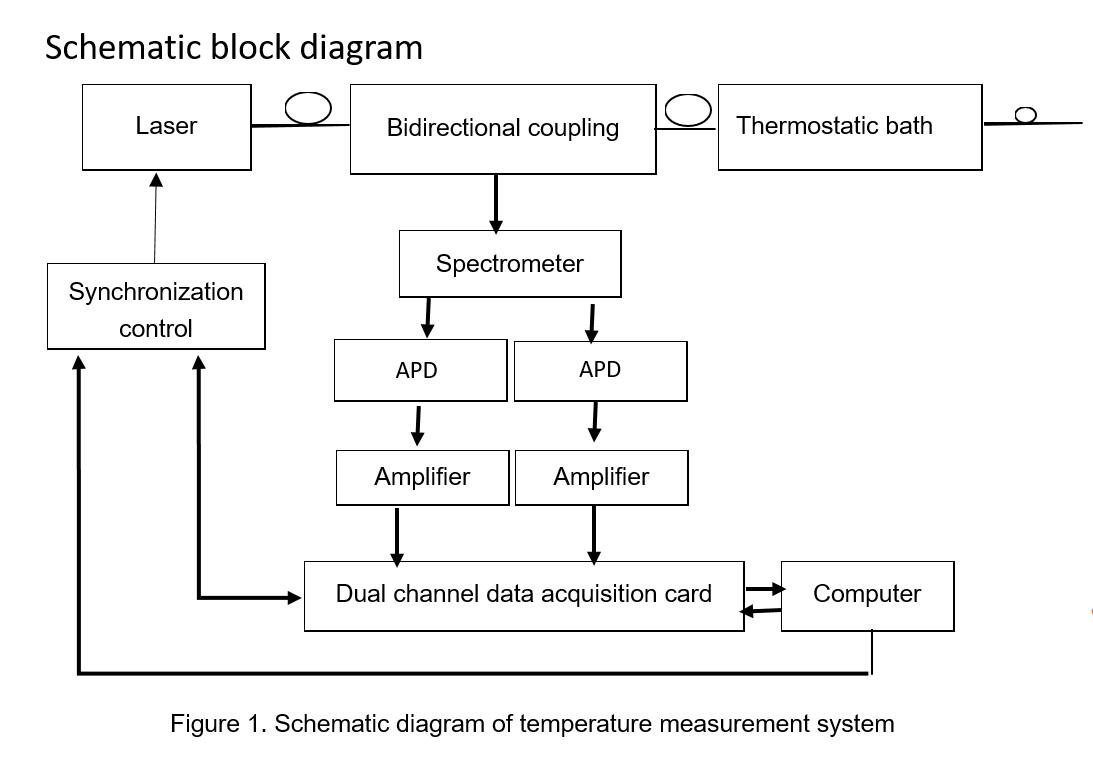
Brief introduction of principle
The data are collected by high-speed acquisition card, processed to remove noise interference and accumulation, and then accurate temperature data can be obtained. The practicability of this system is that it can monitor the temperature data along the optical fiber in real time and at a fixed point. The temperature measurement method of distributed optical fiber temperature measurement system is determined by studying the relationship between Stokes light / anti Stokes light produced by Raman scattering and temperature. And the signal is processed by wavelet transform to remove noise and weak signal.
Method of calculation
The Raman scattering effect can be explained by the interaction and energy transfer between incident light and scattering medium. When the incident light collides with the scattering medium inelastically, the incident light can emit or absorb a high-frequency phonon related to the molecular vibration of the scattering medium. It is called Stokes or anti-Stokes. The wavelength of the long wave side is A. The spectral line of (A。= A。+ △A ) is called Stokes. The wavelength of short wave side is 入. The spectral line of (入。= A。- △A ) is called Stokes. While the Stokes is independent on the temperature, anti-Stokes is dependent on the temperature. By measuring the time difference between the incident light and the reflected light, the distance from the incident end to the position of the scattered light can be obtained. In this way, the distributed measurement is realized.
Recommended model
Emitter: 905nm、1550nm PLD
Receiver: series sar,series IAG
RM 707-708, 258 Guoxia Road, Yangpu District,Shanghai, China PC:200433
Copyright © 2019-2020.Light-Catcher Co.,Ltd All rights reserved.沪ICP备15002270号-1

